Cancer :-
It is uncontrolled division of cell without any differentiation. It is not a single disease rather a group of disease. Some types of cancer cause rapid cell growth, while others cause cells to grow and divide at slower rate.
Certain forms of the disease result in visible growth called tumour, while others such as Leukemia do not.
Tumours :-
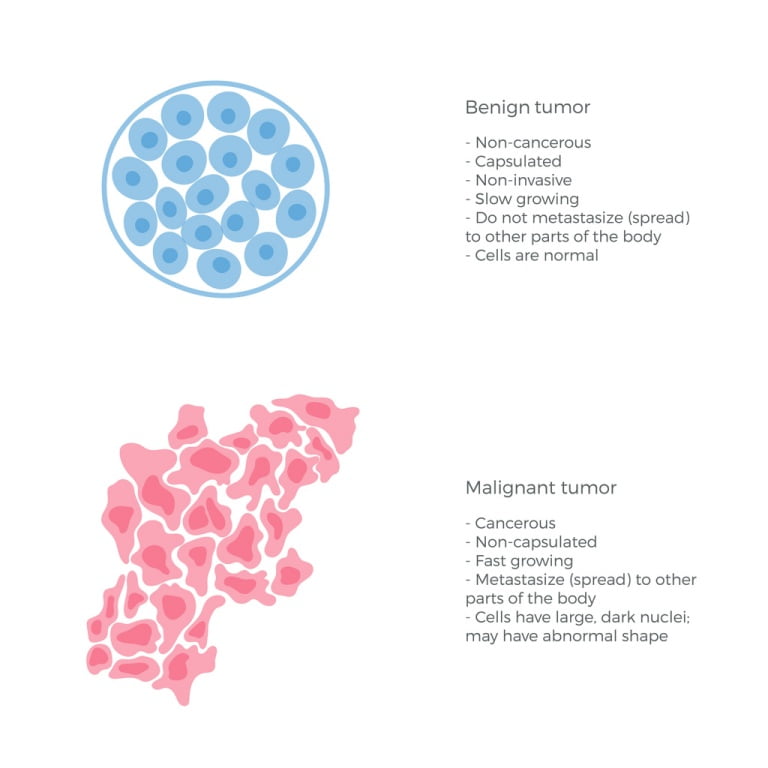
Benign tumour :-
Slow and localised growth, remain confined to the affected organ. They have no latent stage, it cause limited damage to the body.
There is no metastasis (spread ), it is non cancerous and less dangerous.
Metastasis :-
It is transfer of Cancerous cell from one to another part of the body by Blood and lymph vessel.
Malignant tumour ( Cancerous tumour ) :-
Fast and proliferative growth, spread from one to another organ of the body.
They have latent stage, In this case malignant cell migrate from one to another site of the body where they multiply to produce secondary malignant growth.
There is metastasis ( spread ), it is cancerous and more dangerous.
Types of Cancer ( Malignant Tumour ) :-
- Carcinomas.
- Sarcomas.
- Leukemia.
Carcinomas :-
Malignant growth of epithelial tissue that covers or lines the body.
Examples – malignant tumour of breast, lungs, pancreas stomach, cervix, skin and brain.
Sarcomas :-
Malignant growth arising in tissue divided from primitive mesoderm ( connective tissues and muscular tissue ).
Examples – malignant tumour of bone, cartilage, Tendon, adipose tissues, lymph node ( lymphoid tissue ).
Leukemia ( Blood Cancer ) :-
Excessive production of leukocytes in ( WBCs ) by bone marrow.
In India – most common cancer in woman is uterine cervical and most common cancer in man is mouth and throat.
Carcinogen :-
Agent which tend to produce malignant tumour.
- Physical Irritants :-
- Use of Kangri ( in kashmir ) induce abdominal malignant tumour.
- Betel and tobacco chewing induce oral malignant tumour.
- Heavy smoking induced lung’s malignant tumour.
- Jagged teeth may induce tongue’s malignant tumour.
2. Chemical agent :– Target tissue.
coal tar Skin, lungs.
Cadmium oxide Prostate gland.
Aflatoxin Liver.
Mustard gas Lungs.
Ni and Cr compound Lungs.
Asbestos Lungs, pleural memb.
Diethylstilbestrol Vagina.
Vinyl chloride Liver.
3. Radiation agent :-
X – ray, U/V – ray, Radio active radiation.
4. Biological agent :-
Oncogenic virus –
Virus with induces disease ( woman breast cancer have virus life particle in their milk ).
5. Genetic factors :-
It can contribute to the development of the disease. Some genes change proteins that would usually repair damaged cells, It can lead to malignant tumour.
If a parent has these genes, they may pass on the altered instructions to their offspring.
Some genetic changes occur after birth and factors can increase the risk.
Symptoms :-
- A lump or hard area in breast.
- A change in wart or mole, persistent change in digestive and bowel habit.
- persistent cough and hoarseness, excessive loss of blood during monthly period In female or loss of blood outside the usual date.
- Blood loss from any natural orifice.

A swelling or sore throat does not heat easily, unexplained loss of body weight, any ulcer that does not get well.
Diagnosis :-
Biopsy of tissue, Pap test for uterine cervical cancer, Ames test to know the Chemical carcinogen, ELISA test for certain type of disease.
Control :-
Doctors usually prescribe treatments based on the type of malignant cells, it’s stage at diagnosis and person’s overall health.
- Surgery :-
Surgical removal of entire malignant tissue. A Surgeon may remove lymph nodes to reduce or prevent the disease’s spread.
2. Radiation therapy ( radio therapy ) –
Use high dose radiation to kill malignant cells.
3. Chemotherapy –
It’s aims to kill malignant cells. The drugs can also help shrink tumours, but the side effects can be severe.
- Use of anticancerous drug :-
In check the cell division by inhibiting DNA synthesis, it may be more toxic to the malignant cells than normal.
Examples – Vincristine, Vinblastine ( these are used for treatment of leukemia.










