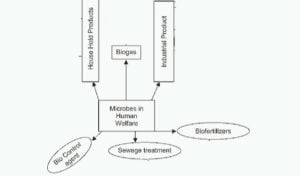
Communicable diseases :-
Communicable diseases are diseases that can transfer from one person to another and caused by microbes like bacteria, protozoa, fungi, viruses, helminthes etc.
Communicable diseases caused by bacteria :-
Tuberculosis, Diphtheria, Whooping cough ( Pertussis ), Cholera, Other diarrheal disease, Leprosy, Tetanus, Gonorrhea, Syphilis etc.
Communicable diseases caused by Viruses :-
Mumps, Measels, Pox, Polio, Trachoma, Rabies, AIDS, Hepatitis COVID – 19 etc.
Communicable diseases caused by Protozoan :-
Malaria, Amoebiasis etc.
Communicable diseases caused by Helminthes :-
Ascariasis , Falariasis, Taeniasis etc.
Transmission, Symptoms, Prevention and Control of Communicable diseases
1. Tuberculosis :-
Disease – Communicable diseases.
Causative agent – Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
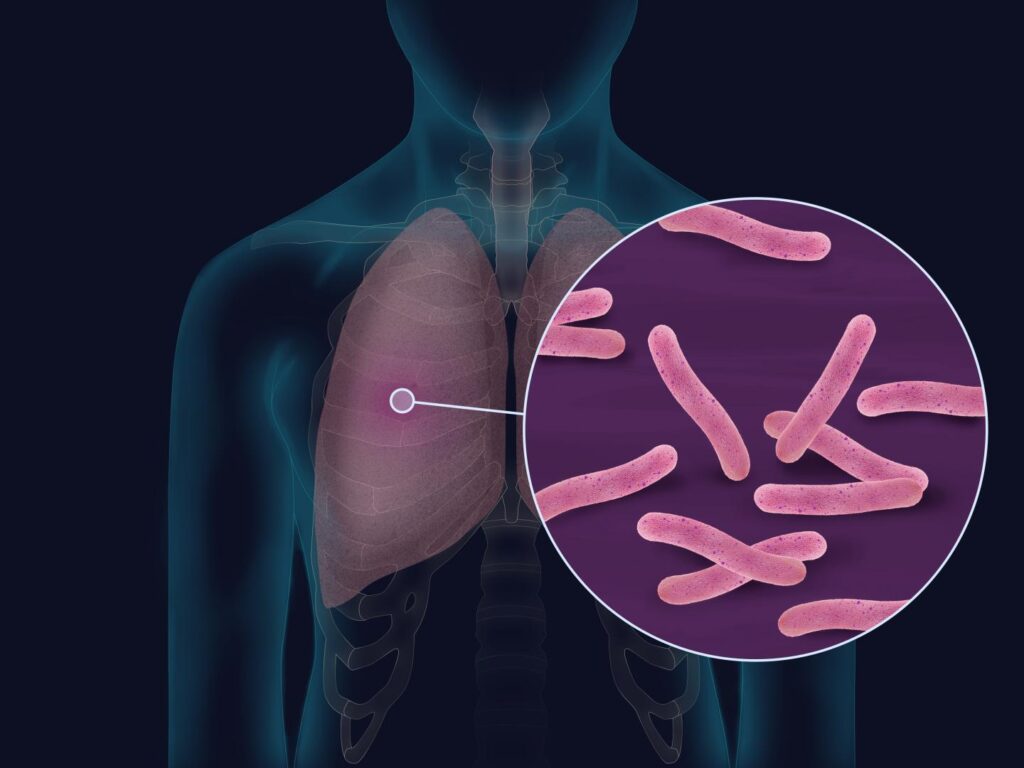
Incubation period – week, Month, Year.
Organ effected- Lungs, intestine, meninges, brain, kidney, cervical lymph node ( in child ).
Diagnosis – By chest X- ray, Tuberculin test, Mantoux test, Sputum examination.
Transmission :-
Air born disease by droplet infection through coughing, sneezing, talking, spitting.
Symptoms :-
Low grade fever, malaise, coughing with expectation, loss of body weight, chest pain
- Bacteria of tuberculosis damaged the tissue, release toxic called tuberculin. Actually tuberculin is antigen structure of mycobacterium tuberculosis, which initiate cell mediated immunity.
Prevention :–
By BCG vaccine, Chemoprophylaxis, Improvement of sanitation, Health promotion.
Control :-
- Use of antibiotic ( Rifampicin, Isoniazid, Ethambutol, Pyrazinamide, Streptomycin ).
- Rest, Surgery may required, Improve nutrition, Health education.
2. Diphtheria :-
It is a communicable disease and more common in children.
Causative agent – Corynebacterium diphtheriae ( Gram positive bacteria ).

Organ effected – Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, Tonsil, Larynx and Heart.
Incubation period – 2 to 6 days.
Diagnosis – Throat swab test, Schick test.
Transmission :-
Air born disease ( Droplet infection and droplet nuclei ).
Symptoms :-
Slight fever, sore throat, pain in throat, respiratory obstruction ( in acute condition ) or chocking of respiratory tract.
- Due to formation of thick tough grey colour membrane in nasopharynx, it’s removal cause bleeding. They formed due to the secretion of semi – solid material by Throat.
- In acute condition, bacteria may go to heart and causes rapid heart block.
Prevention :-
DPT vaccine.
Control :-
Diphtheria antitoxic ( with 24 hours of appearance of symptom ), Antibiotics ( Penicillin, Erythromycin ), Analgesic, Rest and Surgery of throat may required in acute condition.
3. Cholera :-
it is an acute diarrheal disease. In ayurveda it is called vishuchica. It is a communicable disease.
Causative agent – Vibrio cholerae, infection mainly contaminative.
Incubation period – minimum period half hour, 1 to 2 days.
Symptoms :-
Sudden onset of profused effortless, rise, water like a stool followed by vomiting, rapid dehydration, muscular cramp and suppression of urination.
Even death occurs if proper water and electrolyte balance is not taken.
On examination –
signs of dehydration ( pale skin, sunken eye, dry tongue ).
Rapid thready pulse ( weak ).
Blood pressure low, cold extremity.
Prevention :-
By cholera vaccine ( provide immunity up to 6 months ).
Control :-
- To maintain water electrolyte balance in the body.
( a ) ORT ( oral rehydration therapy ) :
WHO formula –
Glucose = 20 gm, KCl = 1•5 gm, NaCl = 3•5 gm, Sodium bicarbonate = 25 gm, Sodium citrate = 29 gm, Water to make = 1 Litre.
Home formula –
First full sugar, 1 chutki salt, water to make 1/2 litre.
( b ) In dehydration in acute then use of intravenous fluid therapy.
2. Antibiotic, Antiemetic, for community – blood sanitation.
Other Diarrheal disease :-
Causative agent :-
- Bacteria – E. coli, Campylobacter, Salmonella.
- Virus – Rotavirus, Echovirus, Enterovirus.
- Protozoa – E. histolytica, Giardia.
Transmission :-
Mainly water borne disease through oral route.
Infection – mainly contaminative stool of patient.
Symptoms :-
Dehydration is common.
In case of shigellosis ( frequent passes of stool with blood, mucus and abdominal cramps ).
Control :-
Maintain water electrolyte balance in the body as in cholera.
Antibiotic in case of bacterial infection, Antiemetic, improve sanitation and water supply, food hygiene.
4. Tetanus ( Lock Jaw ) :-
Causative agent – Clostridium tetani ( Anaerobic, Gram negative bacteria ) ,spore bearing Organism.
- Tetanus is induced by tetanus toxin ( tetanospasmin )
- Bacteria reservoir – Bacilli of tetanus found in intestine of Cattle, Soil dust through Cattle dung.
Incubation period – 6 to 10 days or 1 month.
Mortality – 40 to 80 %
Diagnosis – By symptoms and history.
Transmission :-
Soil born – Spore get attached to the fresh wound by dust and surgical instrument, application of dust over wound, During umbilical cord clumping by khandani chaku
Symptoms :-
Lock Jaw, spasm of back and neck.
Prevention :-
T – toxoid, DPT Vaccine .
Control :-
T – toxoid, ATS, antibiotics ( Penicillin, Erythromycin ), analgesic, good nursing care.
5. Rabies :-
Disease – Communicable diseases.
Causative agent – Rabies virus.
Reservoir host – Dog, Fox, Wolves, Jackals, Mongoose, Bats, Cats, Coyote and Skunks.

Incubation period – Usually 3 to 8 weeks.
Symptoms :-
In human – Hydrophobia ( fear with water ), sore throat, slight fever, headache, malaise.
- In rabid dog – running amuck, change in voice, excessive salivation etc.
- Rabies virus destroy the brain and spinal cord.
- Rabies is the only communicable disease of a human which is 100% fatal if not controlled immediately.
Prevention :-
Vaccination of rabies to dog, other animals and to human being.
- Rabid dog should be kill immediately.
Control :-
Injection of vaccine or ARS or vaccine + ARS to the person after biting of rabid dog.
6. polio :-
Causative agent – polio virus.
Transmission :-
Stages and types :- ( 1 ) Abortive polio – Body ache, fever, malaise.
( 2 ) Non – paralytic polio – Stiffness and pain in neck and back.
( 3 ) Paralytic polio – Damage the alpha – motor neuron of spinal cord mainly.
- Damage of motor neuron, muscle fail to stimulate or contract so the muscle get shrink, painful spasm of muscle.

When the respiratory Center of Brain are attacked by virus.
Result – Nerve impulse to the diaphragm are stopped, breathing fails. In this condition patient needs ‘Iron lungs’ for artificial breathing.
Prevention :-
Polio vaccine – Injectable, Oral.
Control :-
In case of painful muscle spasm –
Good nursing care, steroids, vitamins.
- In chronic stage – Physiotherapy to limb for regain power.
7. COVID – 19 :-
It is an infectious and pandemic disease.
Causative agent – Corona virus ( newly discovered virus ).
Transmission :-
The COVID – 19 virus is spread primarily through droplet or saliva or discharge from the nose when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Symptoms :-
More common – Fever, dry cough and tiredness.
Less common – Aches and pains, sore throat, diarrhoea, conjuctivitis, headache, loss of test or smell, a rash on skin.
Prevention :-
The best way to prevent and slow down transmission is to be well informed about the covid-19 virus, the disease it causes and how it spreads.
- protect yourself and other from infection by washing your hands, social distancing.
Control :-
Stay home from work, school and public area.
- if you have a chronic medical condition and may have a higher risk of serious illness, check with your doctor about other ways to protect yourself.