DNA and it’s structure :-
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid ) is a long polymer of deoxyribonucleotides. The length of DNA is usually defined as number of nucleotides present in it.
This also is the characteristic of an organism.
Example – Bacteriophase known as φ × 174 has 5386 nucleotides, Escherichia coli has 4·6 x10⁶ base pair (bp) and haploid content of human DNA is 3·3 x 10⁹ bp.
- DNA as an acidic substance present in nucleus was first identified by Friedrich Meischer in 1869. He named it as Nuclein.
- In 1953 James Watson and Francis Crick based on the X-ray diffraction data produced by Maurice Wikins and Rosalind Franklin, produced a very simple and femous Double Helix model for the structure of DNA.

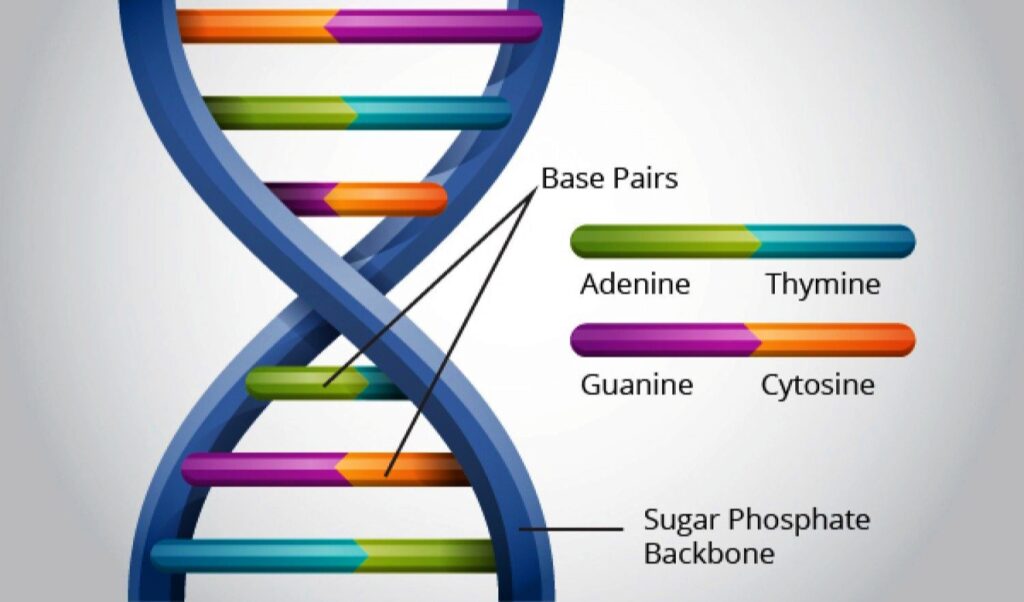
- Double helix structure of DNA is made of two polynucleotide chains where the backbone is constituted sugar-phosphate and base project inside.
- The two chains have anti-parallel polarity. It mesns, if one chain has the polarity 5’→3′ the other has 3’→5′.
- The bases in two strands are paired through hydrogen bond forming base pairs (bp).
Adenine (A) forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine (T) from opposite strand and vice-versa.
Similarly, Guanine (G ) is bonded with cytosine with three hydrogen bonds. As a result always a purine comes to a pyrimidine.
- The two chains are coiled in a right handed fashion. The pitch of helix is 3·4 nm and there are roughly 10 bp in each turn.
- For a double stranded DNA, the ratios between Adenine and Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine are constant and equal to one.
Nucleotide :-

- A nucleotide has three components – a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar ( deoxyribose) and a phosphate group.
- There are two types of nitrogenous bases – Purine (Adenine and Guanine) and Pyrimidine (Cytosine and Thymine or Uracil for RNA). Cytosine is common for both DNA and RNA, Thymine is present in DNA while Uracil is present in RNA at the place of Thymine.
- Two nucleotides are linked togather through 3’→ 5′ phosphodiester linkage to form a dinucleotide, more nucleotides can joined in such a manner to form a polynucleotide chain.
- When a phosphate group is linked to 5′ – OH of a nucleoside through phosphoester linkage, a corresponding nucleotide is formed.
Nucleoside :-
A nucleoside has two components – a nitrogenous base and a pentose sugar.
- A nitrogenous base is linked to the pentose sugar through a N – glycosidic linkage to form a nucleoside. Such as adenosine, guanosine, cyticine and uridine.
Structural formula of purine and pyrimidine :-
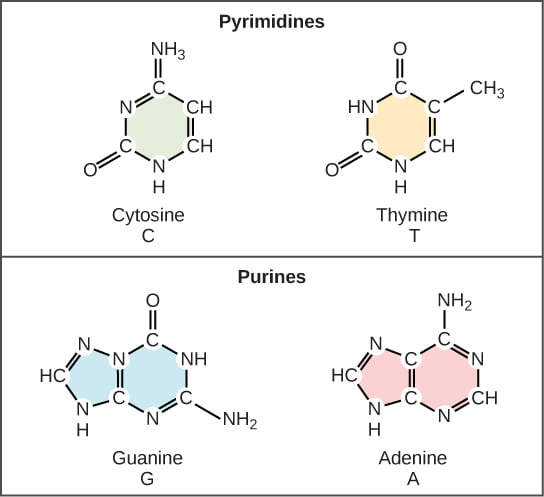
Types of DNA :-
According to modern concept DNA can be following form :-
A-form, B-form, C-form, D-form, E-form and Z-form. In which B-form and Z-form are main.
Differences between B-DNA and Z-DNA.
B-DNA
- Right handed coiling.
- Regular backbone of sugar phosphate.
- 10 base pairs in each helix.
Z-DNA
- Left handed coiling.
- Irregular backbone of sugar phosphate.
- 12 bp in each helix.