Development of Embryo in Flowering Plants :-
Development of Embryo in Flowering Plants occur at the micropylar end of the embryo sac where the zygote is situated .
- Most zygotes divide only after certain amount of Endosperm is formed .
Endosperm :-
During the development of Embryo in Flowering Plants the primary endosperm cell divides repeatedly and form a triploid Endosperm tissue .The cells of this tissue are filled with reserve food materials and are used for nutrition of the developing Embryo .
- Castor and Coconut contains Oily Endosperm .
Types of Endosperm :-
Three main types :-
- Nuclear type :- In nuclear type of Endosperm ,the first division of primary Endosperm nucleus and few subsequent nuclear divisions are not accompanied by wall formation . The nuclei produced are free in the cytoplasm of the Embryo sac and wall formation take place later .
Example – Coconut .
2 . Cellular type :- In this case , there is cytokinesis after each nuclear division of Endosperm nucleus . Thus the Endosperm has a cellular form , from the very beginning because first and subsequent divisions are all accompanied by wall formation .
Example – Petunia , Datura etc .
3 . Helobial type :-
It is an intermediate type between the nuclear and cellular type . The first division is accompanied by cytokinesis but the subsequent ones are free nuclear . The chamber towards Chalazal end .
Development of Dicotyledons Embryo :-
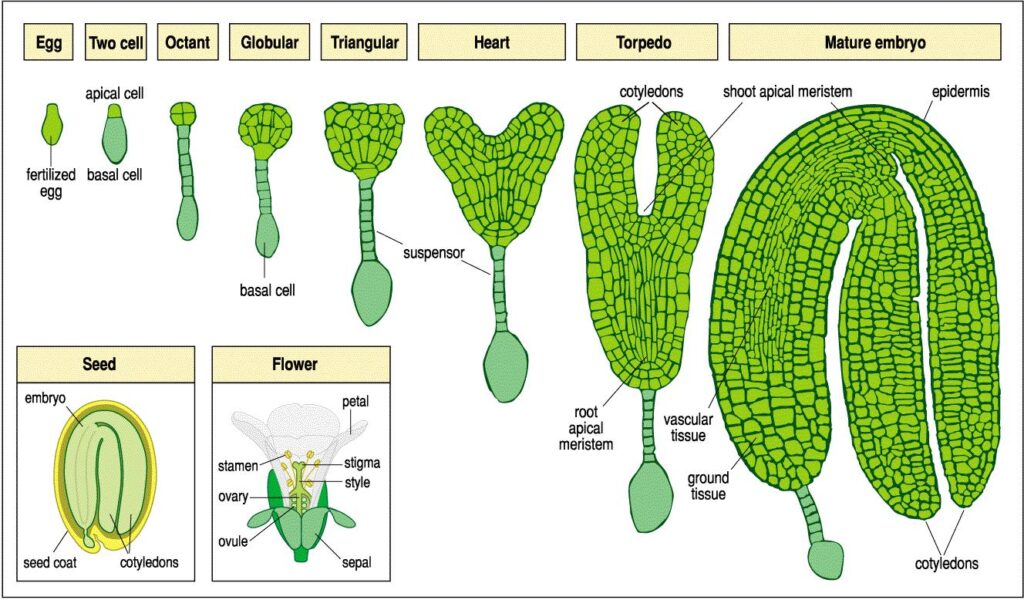
The early stages of development of Embryo in Flowering Plants are similar in both monocotyledons and dicotyledons .
- The zygote gives rise to the proembryo and subsequently to globular , heart shaped and mature Embryo .
- A typical Dicotyledons Embryo consists of an Embryonal axis and two cotyledons .
- The portion of Embryonal axis above the level of cotyledons is the epicotyl with terminates with Plumule or Stem tip .
- The cylindrical portion below the level of Cotyledons is hypocotyl that terminates at it’s lower end in the Radicle or Root tip . The Root tip is covered with a Root cap .
Development of Monocotyledons Embryo :-

During the development of Embryo in Flowering Plants Embryos of Monocotyledons possess only one Cotyledon . In the Grass Family the Cotyledon is called Scutellum that is situated towards lateral of the Embryonal axis .
- At it’s lower end , the Embryonal axis has the Radicle and Root Cap enclosed in an Coleprrhiza .
- The portion of the Embryonal axis above the level of attachment of Scutellum is the epicotyl . It has a Shoot apex .
Also read :- Fertilization & Developement of embryo in humans
Seeds :-

Seeds are basically very small Embryonic Plants that are enclosed by a covering called Seed coat .
A typical Seed Includes three basic components –
- Seed coat :-
The Seed coat refers to the hard or semi hard covering that sheathes a Seed , protective it from fungi , bacteria and various types of diseases .
2 . Cotyledon :-
Cotyledons are the first leaves produced by Plants . They are not considered true leaves and are sometimes referred to as a Seed leaves because they are actually part of the Seed or Embryo of the Plant .
- The Cotyledons are the simple structures generally thick and swollen due to storage of food reserves .
3 . Embryo axis :-
At the same time Embryonic shoot and root develops as well taken together , they are called the Embryonic axis .
- The part of the embryonic axis located above the point of attachment of the Cotyledon is called the Epicotyl .
- The embryonic axis below the Cotyledon attachment site is called the hypocotyl and is the progenitor of the root .
Fruits :-

During the development of Embryo in Flowering Plants like mangoes the transformation of Ovule into Seeds and Ovary into Fruit proceeds simultaneously .
The Fruit primarily contains two parts – the Pericarp and the Seed . the Pericarp layer is actually the outer wall of the Ovary from which the Fruit developed .
- The Pericarp has three layers –
1 . Exocarp or Epicarp :-
This is the outermost layer of Pericarp that forms the skin of the Fruit .
2 . Mesocarp :-
It is the thick , fleshy and juicy middle layer of the Pericarp .
3 . Endocarp :- It is the innermost layer of the Fruit which often develops into the Pith .
True Fruits :-
It is the Fruit that is formed from the fertilized Ovary of the Flower and Ovules get transformed into Seeds .
- True Fruits are made up of two parts namely Pericarp and Seed .
- True Fruits can be simple Fruits , Aggregate Fruits and Multiple Fruits .
- Based on the Pericarp simple Fruits can be classified into two types which include Fleshy Fruits Dry Fruits .
Fleshy Fruits :- Examples – Mango , Berry , Grape ,Orange etc .
Dry Fruits :- Examples – Achene , But Grain Samara etc .
Aggregate Fruits :- Example – Raspberry ,
Multiple Fruits :- Examples – Mulberry , Figs etc .
False Fruits ( Parthenocarpy ) :-
It is the phenomenon in which Fruits are formed without Fertilization .
Fals Fruits arises from other Floral parts except the Ovary .These Fruits are Seedless .
Examples – Apple , Pineapple , Banana ,Strawberry , Akharot , kaju etc .