Applications of Biotechnology :-

Applications of Biotechnology in –
1 . Alcohol production .
2 . Dairy products formation .
3 . Organic acids formation .
4 . Enzymes production .
5 . Vitamins production .
6 . Antibiotics production .
7 . Vaccines production .
8 . Hormones production .
9 . Recombinant DNA technology .
10 . Steroids production and
11 . Applications of Biotechnology in Agriculture .
Applications of Biotechnology in Alcohol production :-
Used of micro organism like Yeasts or Yeast like organism in alcoholic fermentation or Yeast fermentation .
Fermentation :- First reported by Louis Pasteur , Reported that alcohol , beer , butter milk , are result of yeast fermentation .
- Fermentation process is completed with the help of enzymes produced by yeast . These Enzymes are Invertase , Zymase .
Common products of Yeast / Alcoholic fermentation :-
( a ) Beer :- Produced from barley malt , alcohol contains 4 – 8 ℅
( b ) Wine :- From Fruit juices specially grapes or sometimes apples , oranges . Alcohol contains 10 – 20 ℅
( c ) Brandy :- From fruit juice by distillation of wine . Alcohol contains 43 – 57 ℅
( d ) Rum :- From sugarcane , alcohol contains 40 ℅
( e ) Whisky :- From fermented cereals like maize , wheat . Alcohol contains 25 – 35 %
Applications of Biotechnology in Dairy products formation :-
Youghurt / Yogurt , Cheese , Whey etc .are dairy products .
Yogurt :-
Yogurt is a special diet semi solid preparation , produced by curdling of milk with the help of curdling culture at 4o – 46⁰c for four hours .
Lactobacillus bulgaricus , Streptococcus lactis these micro-organisms ( bacteria ) secretes enzyme lactase . Milk contains lactose sugar is converted into lactic acid with the help enzyme lactase , coagulates milk protein casein and forms Curd .
- For sweetening and flavour Fruits mixed with Yogurt .
- Yogurt is more useful because of the process of additional vitamins produced by bacteria , Yeast etc .
Cheese :-
Cheese is a product of curdling fermentation . It is a nutritive product which contains – proteins 22 to 35% , vitamins small amount and fats 20 to 30% .
- It is formed by the curdling of milk with the help of lactic acid bacteria followed by addition of sheep or goat stomach as a source of rennet enzyme .
- Cheese producing enzyme was first extracted by C . Hansen from Calf’s stomach .
- Cheese may be soft or hard , soft cheese contains more than 40% moisture while hard cheese contains less than 40% moisture .
Applications of Biotechnology in organic acid production :-
Common acids :-
1 . Lactic acid . – First organic acid produce through fermentation .
- sources – From the fermentation of corn starch , molasses , potato , whey .
- Agent / microbes – Streptococcus , Lactobacillus .
- Uses – preservative .
- 2 . Acetic acid –
- Sources – From the fermentation of sugarcane juice .
- Agent / microbes – Yeast , Acetobacter aceti .
- Uses – used in pharmaceuticals used as colouring agent .
- 3 . Citric acid . –
- Sources – From the fermentation of molasses in beet root .
- Agent/ microbes – Aspergillus niger , Yeast .
- Uses – used in dying .
4 . Gluconic acid . –
- Sources – From the Oxidation of Glucose .
- Agent / Microbes – Aspergillus niger , Penicillium species .
- Uses – used in pharmaceuticals .
5 . Gallic acid . –
- Sources – From the Oxidation of Glucose .
- Agent / Microbes – Aspergillus niger .
- Uses – used in Ink making .
Applications of Biotechnology in enzyme production :-
Enzyme Rennet first isolated by Hansen from Calf’s stomach .
- Enzyme Diastase first isolated by Persoz and Pyren from germinating Barley grain . ( fermentef malt ) .
- Total Enzymes discovered – about 2200 but only a few about 250 enzymes used in industries , medicines and and food productions .
Common Enzymes from Applications of Biotechnology :-
1 .Protease ( proteolytic enzyme ) :-
- Sources – From Aspergillus oryzae , Bacillus subtilis .
- Uses – used in detergent and remove some proteinaceous cloth .
2 .Amylase :-
- Sources – Bacillus subtilis , Aspergillus oryzae , Aspergillus niger.
- Uses – used to bread making , for softening of starched cloth .
3 . Papain :-
- Sourses – From latex of papaya .
- Uses – used for making the meat tender .
4 . Pectinase :-
- Sources – From Aspergillus luchuensis .
- Uses – used for destruction of Penicillium .
5 . Rennet :-
- Sources – From Calf’s stomach .
- Uses – used for cheese preparation .
6 . Thrombin :-
- Sources – From blood plasma .
- Uses – uses for blood clotting in surgical operations .
7 . Cellulase :-
- Sources – From Myrothecium verrucaria .
- Uses – used in production of Dextrin and Fructose .
Applications of Biotechnology in vitamins production :-
Vitamin was first discovered and Vitamin term given by Funk .
- Vitamins are an organic compound needed in a small amount ( either produced by cell or provided along with food diet ) and regulate as well as catalyse various metabolic activities of living organisms .
Discovery of some Vitamins :-
1 . Vitamin B₁ ( Thiamine ) – First discovered by Funk .
- Deficiency disease – Beri- beri .
2 . Vitamin C ( Ascorbic acid ) – First discovered by Gyorgy .
- Deficiency disease – Scurvy .
3 . Vitamin A ( Ratinol ) – First isolated by Mecullum .
- Deficiency disease – Night blindness .
4 . Vitamin D ( Calciferol ) – First isolated by Mellarby .
- Deficiency disease – Ricketi .
Total Vitamins – about two dozen .
Fat soluble Vitamins –
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
Water soluble Vitamins –
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin B complex
Vitamin B complex –
- Vitamin B₁ ( Thiamine )
- Vitamin B₂ ( Riboflavin )
- Vitamin B₃ ( Pantothenic acid )
- Vitamin B₅ ( Niacin )
- Vitamin B₆ ( Pyridoxine )
- Vitamin B₁₂ ( Cobalamine )
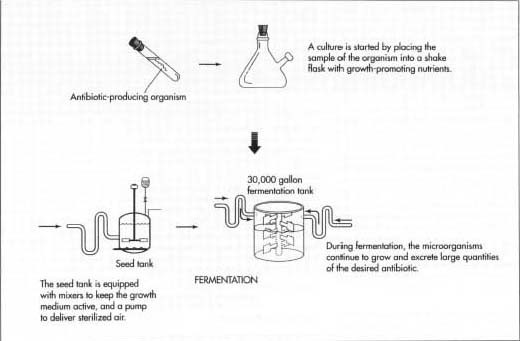
Applications of Biotechnology in antibiotic production :-
A substance of microbial origin with antimicrobial activity . A chemical substances secreted by one microorganism checks the growth of another microorganism .
- Term antibiotic used by Waksman , he discovered two antibiotics – Streptomycin and Actinomycin .
- First discovered antibiotic – Penicillin , discovered by Alexander Flemming .
Source of Antibiotics :-
Fungi , Bacteria .
Total Antibiotics – about 7000
- Broad spectrum Antibiotics – inhibits many pathogenic species .
- Narrow spectrum Antibiotics – inhibits an specific pathogenic species .
Common antibiotics and microbial source :-
Bacterial origin –
1 . Subtilin .
- Source – Bacillus subtilis .
2 . Polymyxin .
- Source – Bacillus polymyxa .
3 . Streptomycin .
- Source – Streptomyces griseus .
4 . Chloromycin .
- Source – Streptomyces venezuelae.
5 . Terramycin .
- Source – Streptomyces rimosus .
6 . Aureomycin .
- Source – Streptomyces aureofaciens .
7 . Erythromycin .
- Source – Streptomyces erythraeus .
8 . Neomycin .
- Source – Streptomyces fradiae .
Fungal origin –
9 . Penicillin .
- Source – Penicillium notatum .
10 . Ergotine .
- Source – Claviceps purpurea .
11 . Grieseofulvin .
- Source – Penicillium grieseofulvum .
12 . Citrinin .
- Source – Penicillium citrinin .
Applications of Biotechnology in Vaccines production :-
Vaccine is liquid dead , attenuated form . It can be injected or taken orally to provide immunity towards that pathogens .
- Vaccine was discovered by Edward Jenner ( 1796 ) against small pox .
- First generation Vaccines – they are obtained by conventional technique involving killing or weakening of the pathogen but they have side effects .
- Second generation Vaccines – they are ones made of pure antigen of the pathogen only which are multiplied through Genetic engineering . Example – Vaccine against Hepatitis B .
- Third generation Vaccines – They are purest , highest potency Vaccines which are synthetic in nature .
Applications of Biotechnology in Recombinant DNA technology :-
Used in synthesis of useful products
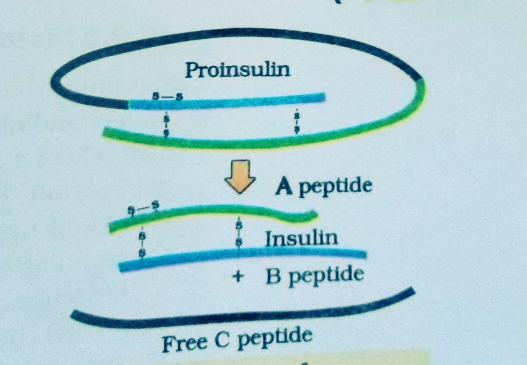
1 . Insulin ( Humulin ) :-

DNA technology .
2 . Human growth hormone ( GH ) :- These hormone secreted by anterior pituitary gland .
Deficiency cause Dwarfism . GH can be synthesised through Recombinant DNA technology where DNA / Genes needed for the synthesis of GH . First synthesised and then integrated with bacterial plasmid to produce required amount of hormones ( GH ) .
3 . Interferon :- Antiviral protein I . e . checks viral growth synthesised by viral infected host cell . interact with neighbouring non – infected cells and makes them resistant to viral attack .
- Interferon synthesised by Genetic engineering are effective against influenza virus , Hepatitis virus etc .
Applications of biotechnology in Agriculture :-
Applications of biotechnology for increasing food production –
1 . Agro-chemical based agriculture .
2 . Organic agriculture and
3 . Genetically engineered crop based agriculture .
The Green Revolution succeed in tripling the food supply but yet it was not enough to feed the growing human population . Increased yields have partly been due to the use of improved crop varieties , but mainly due to the use of better management practices and use of Agrochemicals ( fertilizers and pesticides ) .
However , for farmers in the developing world , Agrochemicals are often too expensive , and further increases in yield with existing varieties are not possible using conventional breeding .
- There are alternative path that our understanding of genetics can show so that farmers may obtain maximum yield from their fields .
- Use of genetically modified crops is a possible solution .
- Plants , bacteria and animals whose genes have been altered by manipulation are called Genetically Modified Organisms ( GMO ) .
GM plants have been useful in many ways . Genetically modified has –
1 . made crops more tolerant to abiotic stress ( cold , drought , salt , heat ) .
2 . reduced reliance on chemical pesticides ( pest resistant crops ) .
3 . help to reduce post harvest losses .
4 . increased efficiency of mineral used by plants ( this prevent early exhaustion of fertility of soil ) .
5 . enhanced nutritional value of food , example – vitamin A enriched rice .
- Some of the applications of biotechnology in agriculture that I will study in detail for the production of pest resistant plants , which could decrease the amount of pesticide used .
BT toxin is produced by a bacterium called Bacillus thuringiensis ( Bt ) .
- BT toxin gene has been cloned from the bacteria and been expressed in plants to provide resistance to insects without the need for insecticides , in effect created a Bio -pesticide .
Examples are BT Cotton , BT corn , rice , tomato , potato and soybean etc .
BT cotton :-
Some strains of Bacillus thuringiensis produce proteins that kill certain insects such as lepidopterans ( tobacco budworm , armyworm ) , coleopterans ( beetles ) and dipterans ( flies , mosquitoes ) .
- B . thuringiensis forms protein crystals during of particular page of their growth . These crystals contain a toxic insecticidal protein .
- Specific BT toxin genes were isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis and incorporated into the several crop plants such as cotton .
The toxin is coded by a gene named cry . There are a number of them , for example , the proteins encoded by the genes cryIAc and cryIIAb Control the Cotton bollworms , that of cryIAb controls corn borer .

Applications of biotechnology in Pest Resistant plants : –
Several nematode parasitise wide variety of plants and animals including human beings . A nematode Meloidegyne incognittia infects the roots of tobacco plants and causes a great reduction in yield .
- A novel strategy was adopted to prevent this infestation which was based on the process of RNA interference ( RNAi ) .
- RNAi takes place in all Eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defence . this method involves silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA molecule that binds to and prevents translation of the mRNA .
- Using Agrobacterium vectors , nematode specific genes were introduced into the host plant . The introduction of DNA was such that it produced both sense and anti -sense RNA in the host cells .



