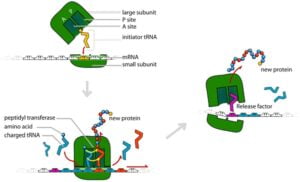
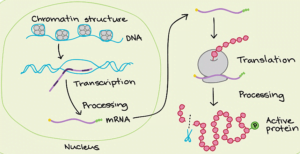
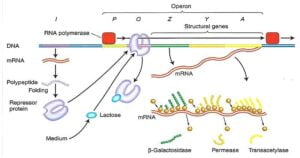
Allele or Allelomorph :-
Genes which code for a pair of contrasting traits are known as alleles, i.e. They are slightly different forms of the same gene.
Example – In case of the character of height, T is used for the tall trait and t for the dwarf, T and t are alleles of each other.
Hence, in plants the pair of alleles for height would be TT, Tt and tt.
Pleiotrophic gene :-
Genes which govern more than one characters of function is called pleiotrophic gene.
Genotype :-
Struture of genes of an organism is called genotype.
Example – TT, Tt and tt for height.
Phenotype :-
It is a physical expression of the genotype or external form of any trait is called phenotype.
Example – Tall for TT and Tt, Dwarf for tt, Round for RR and Rr.
Dominant characters ( traits ) :-
A dominant trait is an inherited characteristic that appears in an offspring if it is contributed from a parent through a dominant allele ( represent capital latter ). Traits, also known as phenotypes.
- This trait will always be expressed in the offspring if the dominant allele is present even if there is only one copy of it ( heterozygous or homozygous )
Representation of dominant traits –
Aa ( heterozygous )
AA ( homozygous )
Recessive traits :-
A recessive trait will only be expressed of the recessive allele that codes for the trait ( recessive homozygous – aa, rr, tt etc )
Homozygous :-
If an individual carries the same two alleles for a gene, they are homozygous.
Example – aa, AA, TT, tt etc.
Heterozygous :-
If the two alleles are different, the individual is called heterozygous.
Example – Aa, Tt, Rr etc.
First generation or F₁ – generetation :-
The generation formed by the hybridisation ( cross ) between two parents is called first generation.
Second generation or F₂ – generation :-
The generation formed by the cross between two organisms of F₁ – generation is called F₂ – generation.
Emasculation :-
The process of pik-out to the anther from a flower before maturation is called Emasculation.