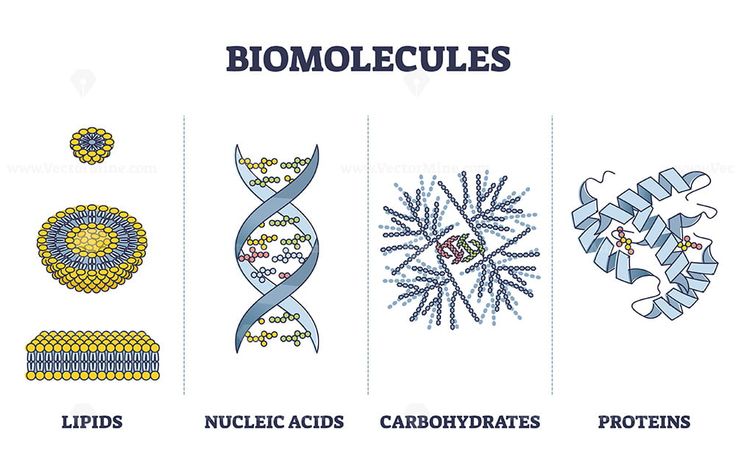
Biomolecules :-
All the carbon compounds that we get from living tissues can be called biomolecules.
e. g. – Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic acids, Lipids, Enzymes etc.
Primary metabolites :-
Found in animal tissues.
e.g . – Amino acids, Sugars and Lipids
Function : – Normal body functions, growth and development.
Secondary metabolites :-
Mainly found in plants, fungi and microbes.
e.g. – Alkaloids, Flavonoids, Rubber, Oils, Antibiotics, Pigments, Spices etc.
Functions :-
- Producing organisms is often unknown.
- Useful to humans for making medicines, perfumes and other products.
types of Biomolecules :-
Two types –
1. Biomicromolecules.
2. Biomacromolecules
Biomicromolecules :-
Small biomolecules with molecular weight less than 1000 Da (Dalton), found in acid soluble pool.
e.g. – Amino acids, Fatty acids, Nucleotides, Monosaccharides and Nitrogenous bases.
Biomacromolecules :-
Larger biomolecules, compounds with molecular weight above 10,000 Da are found in acid insoluble fraction.
e.g. – Proteins, Nucleic acids and Polysaccharides.
Amino acids :-
Amino acids are organic compounds containing an amino group, carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and an R-group.
- An amino group and an acidic group as substituents located on the same carbon i.e. alpha carbon.
- General formula for an amino acid is –
R-CH(NH2)-COOH Or
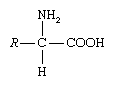
Types of Amino acids :-
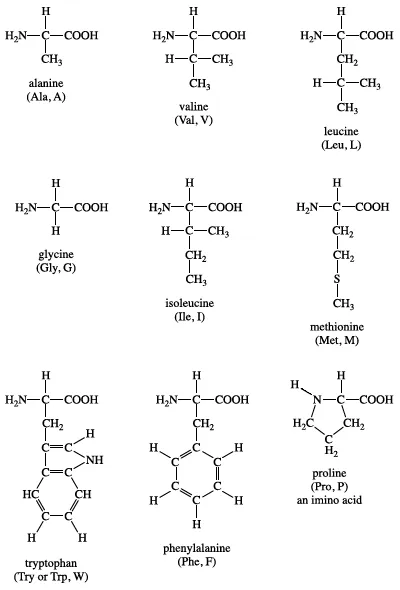
- Based on the nature of alkyl group (R), proteins occur 20 types of amino acids.
- Based on number of Amino and Carboxyl groups, these are 3 types –
I. Acidic amino acids :- e.g. – glutamic acid
II. Basic amino acid :- e.g. – lysine
III. Neutral amino acid :- e.g. – valine
- Amino acids can be aromatic :- e.g. – tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophan
Structures of amino acids :-
Lipids :-
Lipids are generally water insoluble and can be simple fatty acids, glycerol or both fatty acids and glycerol.
A fatty acid has a carboxyl group attached to an R group.
- Fatty acids can be saturated ( without double bond) or unsaturated (with one or more C=C double bonds).
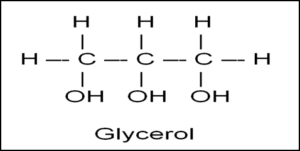
Glycerol is a Trihydroxy propane.
Formula :- C3H8O3
- The fatty acids are found esterified with glycerol. They can be monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides.
Lipids are also called fats and oil based on melting point.
- Oils have lower melting point (e.g. – gingelly) and remain as oil in winters.
Structure of fats and oils (triglycerides) :-
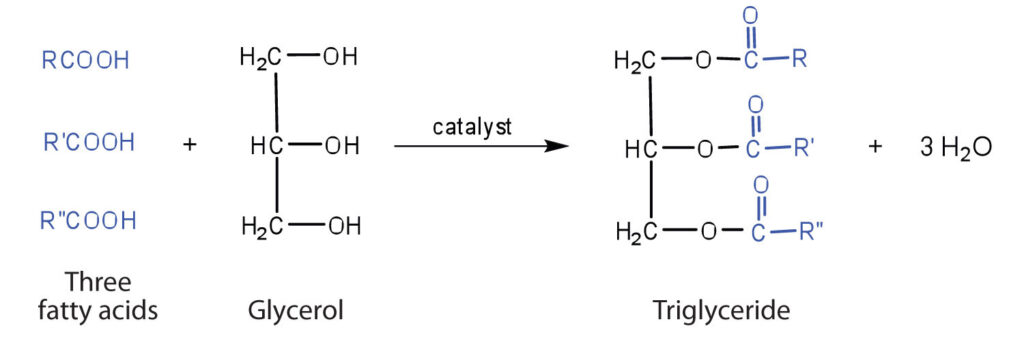
Some lips have phosphorus and a Phosphorylated organic compounds called phospholipids.
- Phospholipids are found in cell membrane. e.g. – Lecithin.
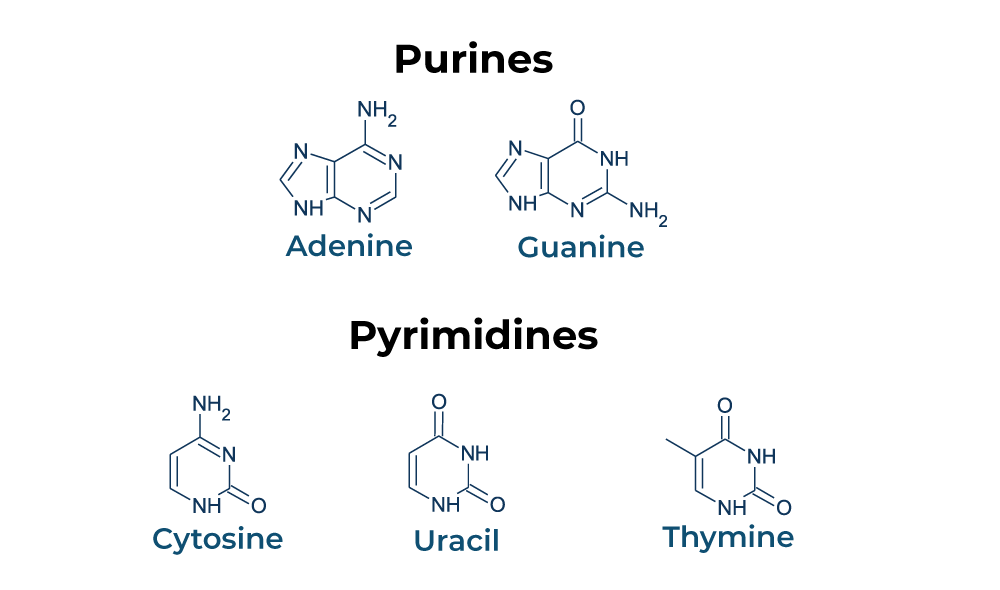
Nitrogenous bases :-
These are carbonic compounds of heterocyclic rings.
Types :- Two
- Purine – having two molecules (Adenine and Guanine)
- Pyrimidine – having two molecules (Thymine/Uracil and Cytosine)
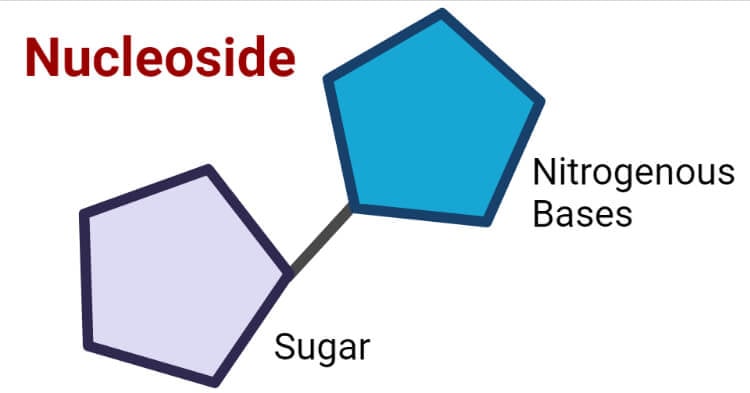
Nucleoside :-
When nitrogenous bases attached with pentose sugar (contains 5 Carbons) then forms nucleosides.
e.g. – Adenosine, Guanosine, Thymidine, Uridine and Cytidine.
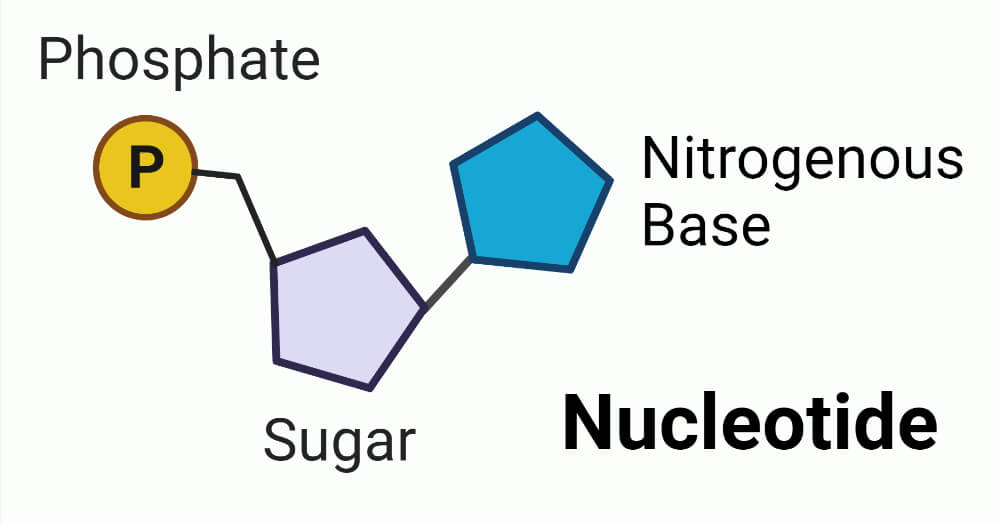
Nucleotide :-
In a nucleotide, a phosphate group esterified with sugar then the new molecule is called nucleotide.
e.g. – Adenylic acid, Thymidylic acid, Guanylic acid, Uridylic acid and Cytidylic acid.
Nucleic acid :-
Made up of one or two polynucleotides (a chains of nucleotides) chains.
- Found in the nucleus of a cell.
- Carry genetic information from parents to their offsprings, so called genetic materials.
Types – two
- DNA (Deoxyribose nucleic acid) :- having two polynucleotides
- RNA (Ribonucleic acid) :- having single polynucleotide.
Proteins :-
Proteins are polypeptide chans. It is polymer of amino acids.
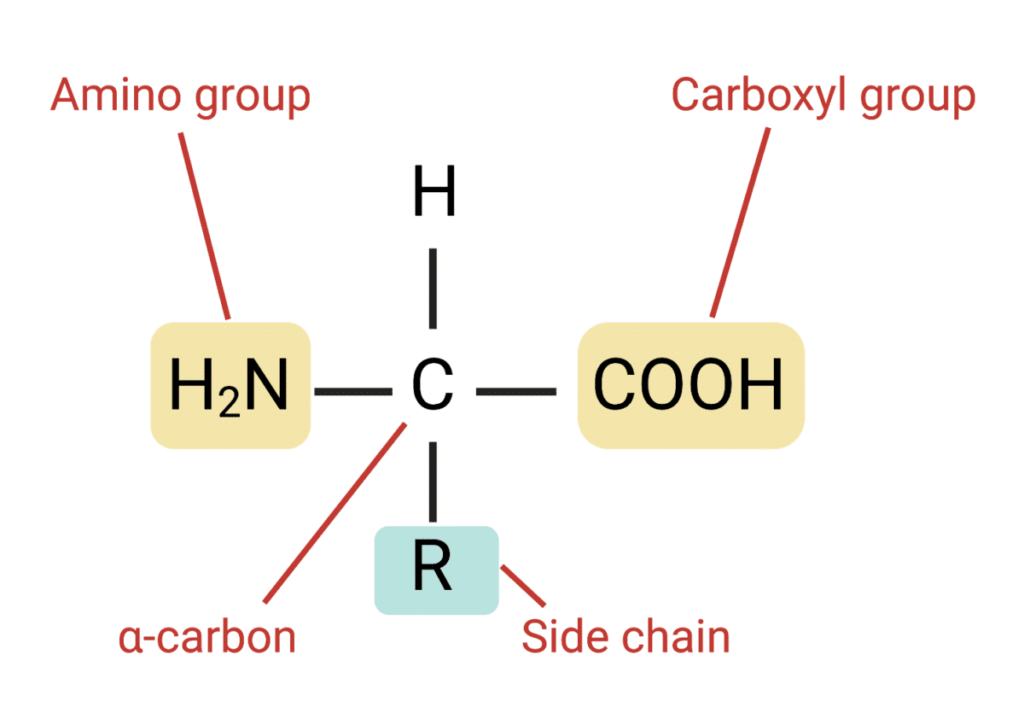
Structure of amino acid.
There are 20 types of amino acids.
e.g. – alanine, cysteine, proline, tryptophan, lysine etc.
When many amino acids are joined together they result in the formation of polypeptides.
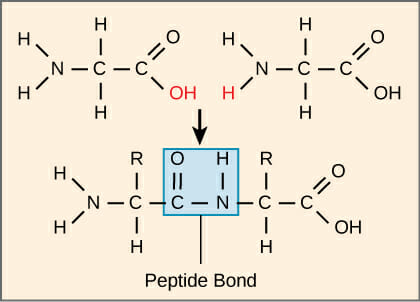
Formation of peptide bond.
Protein structure :-
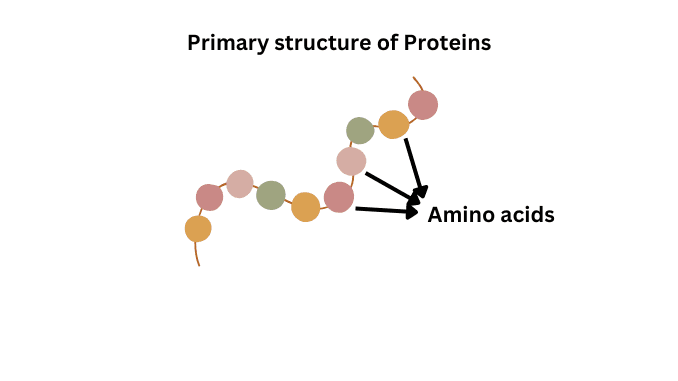
1. Primary structure :-
This structure of protein consists of the amino acids sequence that is joined together by a peptide bond.
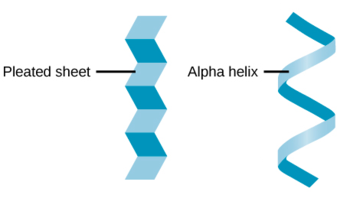
2. Secondary structure :-
Hydrogen bonds between the backbone atoms of the polypeptide chain cause it to fold into specific repeating structures.
- It includes alpha – helix (coild structure) and beta – sheets (folded, sheet like).
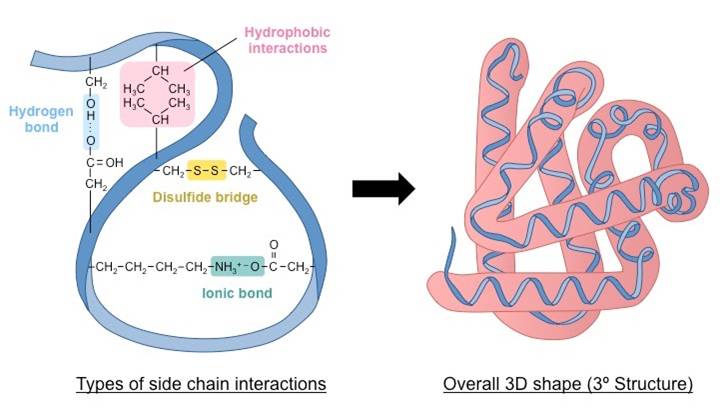
3. Tertiary structure :-
A three dimensional structure of protein due to the interaction between the primary structure and its side chains.
- Interaction include hydrophobic, hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and covalent bonds.
4. Quaternary structure :-
They are made up of two or more polypeptide chains that are joined together with the help of hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, electrostatic interaction etc.

e.g. – haemoglobin.
5. Fibrous and Globular proteins :-
Fibrous proteins, like collagen and keratin, are typically long, thread-like structures that provide structural support and protection.
Globular proteins, like enzymes and hormones, are more compact and spherical, involved in various dynamic cellular processes.
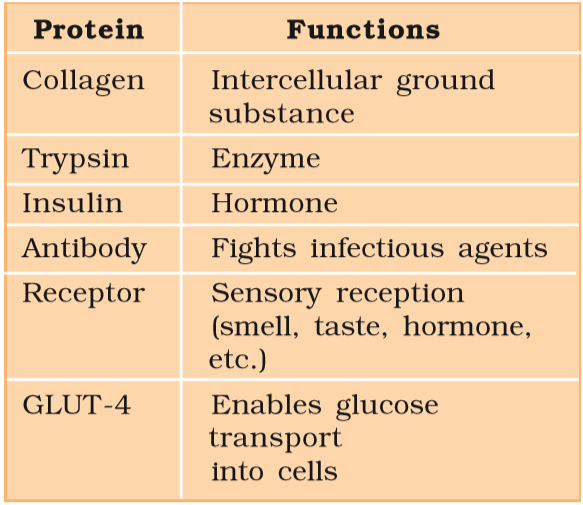
Some proteins and their functions :-
Enzymes :-
Enzymes are made up of proteins and consist of various structures like proteins that include the primary, secondary and tertiary structures.
- The enzyme consists of an active site that helps in binding the substrate molecule.
Properties of enzymes :-
- All enzymes are proteins but all proteins are not enzymes.
- For each substrate, the enzymes are specific.
- Enzymes function as catalysts.
- They are six manor types – Oxidoreductase, Transferases, Lyases, Ligases and Isomerases.
- For an enzymes to function, some of them require a Co-factor or Co-enzyme to function.